Zero Trust Security is a cutting-edge approach to cybersecurity that is becoming essential in 2024. It verifies every access request continuously, ensuring only authorized users can access sensitive information. As cyber threats become sophisticated, Zero Trust Security provides a robust defense by focusing on strict access controls and constant monitoring. This makes it the next big thing in protecting data and systems in today’s digital world.
What is Zero Trust Security in 2024?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity approach in which every user, inside or outside the organization’s network, must be checked and verified before accessing apps and data. It works on the idea that all network activity is considered suspicious until it’s confirmed safe, moving away from the old way of “trust but verify.”
Some Key Points

- Over 80% of cyber attacks happen because of the use or misuse of credentials within a network.
- You can implement Zero Trust Security in several ways, such as Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA).
- Gartner explains ZTNA as a method that limits access through a trusted middleman, verifying the user’s identity, context, and policy adherence before granting access.
- The Zero Trust Essentials series by Microsoft Mechanics has five episodes that cover six key areas of protection: identities, devices (endpoints), applications, data, infrastructure, and networks.
The Rapid Growth of the Zero Trust Security Market:
The researchers expect the global Zero Trust security market to grow from almost $32 billion in 2023 to nearly $133 billion by 2032. This shows a big shift as more companies start using this security model.
According to Gartner, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) has increased by 60% yearly as organizations see its benefits. Companies that have fully implemented Zero Trust security save an average of 43% on costs related to data breaches.
The average breach cost for organizations without Zero Trust is $5.04 million, but for those with total Zero Trust in place, it drops to $3.28 million. Zero Trust helps prevent security breaches by removing automatic trust within the system and requiring checks at every access point.
It also gives detailed control over access to cloud and container environments, reduces the damage from successful attacks, and helps meet compliance requirements. Using the Zero Trust framework, organizations can greatly reduce the risk of attackers moving freely within the network, limiting their access to sensitive areas.
5 Pillars of Zero Trust Security
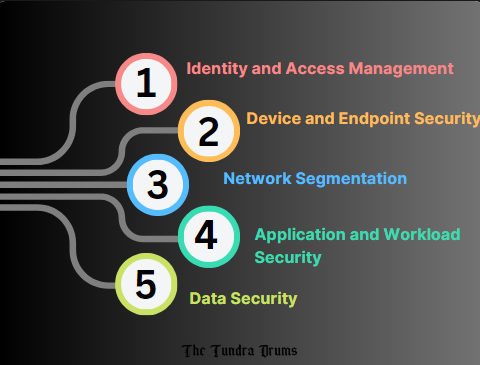
These five pillars provide a comprehensive Zero Trust Security framework that minimizes the attack surface and improves overall cybersecurity by verifying trust at every step.
1. Identity and Access Management:
- Make sure that every user and device is properly verified and continuously checked when they access the network.
- Use a centralized system to manage identities and enforce strong multi-factor authentication that resists phishing attacks.
- Restrict access based on user roles and the principle of least privilege, meaning users only get the minimum access they need to do their jobs.
2. Device and Endpoint Security:
- Ensure that all devices meet security standards with the latest software updates and no unauthorized components.
- Use tools like mobile device management (MDM) to control mobile devices, trusted platform modules (TPMs) for security hardware, and continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to threats.
- Lock down devices when there is any unusual activity and update them with the latest security patches.
3. Network Segmentation:
- Divide the network into smaller sections to protect important business operations from potential threats.
- Monitor and control these segments to reduce the risks of cyberattacks.
- Apply detailed access controls and use micro and macro segmentation to manage who can access different network parts.
4. Application and Workload Security:
- Protect all applications and their resources, such as servers and data storage.
- Limit application access so they can only reach the resources they need to operate.
- Use proxy technologies to add a layer of security to applications.
5. Data Security:
- Identify, categorize, manage, and secure all stored or transmitted data.
- Restrict data access based on the least privilege principle so that only those who absolutely need access have it, and encrypt data when you are not using it.
- Continuously monitor for any threats to the organization’s sensitive data to keep it safe.
What is Zero Trust Data Protection?

Zero Trust Data Protection (ZTDP) is a security strategy that uses the principles of Zero Trust to keep data safe. It operates on the idea that no user, device, or application should be trusted automatically. The main rule of Zero Trust is “Never Trust, Always Verify.” This means every request to access data must be checked and approved, ensuring users only get the access they need.
Key Features of Zero Trust Data Protection
- Continuous Authentication: Every time someone tries to access data, their identity is verified. This ensures that only the right people can see or use sensitive information.
- Least Privilege Access: Users are only given the minimum level of access needed to perform their tasks. This helps prevent unauthorized access and misuse of data.
- Contextual Awareness: Decisions about who can access data are made based on various factors, such as the user’s identity, the type of data, and the environment from which the request is made.
- Data-Centric Security: Instead of securing the network, Zero Trust Data Protection focuses on securing the data.
- Policy Enforcement: Access to data is controlled based on specific rules about the data, the user, and the security context at the time. This applies to all types of data, whether stored or transferred.
How to Implement Zero Trust Data Protection?
If your organization wants to adopt Zero Trust Data Protection, here are some steps to consider:
- Granular Access Controls: Create detailed rules about who can access data types and under what conditions.
- Data Classification: Identify and categorize data based on its sensitivity and importance so you can apply the proper security measures.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Monitor how data is accessed and used to spot unusual activity quickly and respond to potential threats in real time.
- Integration with Existing Security Measures: Zero Trust Data Protection should work with your current security systems to improve overall data security without causing disruptions.
Benefits of Zero Trust Data Protection
- Enhanced Security: By using Zero Trust principles to protect data, organizations can greatly reduce the chances of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Improved Compliance: This approach helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by ensuring that data access is controlled and monitored.
- Flexibility for Remote Work: Zero Trust Data Protection offers a solid framework to secure data across various environments as more companies move to remote work and cloud-based solutions.
How Zero Trust Security Protects Your Data in 2024?

In 2024, Zero Trust Security protects your data by continuously verifying every user’s identity. It accesses requests regardless of their location or device. It operates on the “Never Trust, Always Verify” principle. Instead, access to data is tightly controlled based on who the user is, what they need to access, and the security context. This approach ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data. It reduces the risk of breaches and keeps your data secure across all environments, including remote and cloud-based systems.
What is the Future of Zero Trust?
Zero Trust security has evolved significantly in 2024 as organizations face more complex cyber threats and technological changes. Here are the key trends shaping its future:
- Integration with AI:
- Enhanced Threat Detection: AI will improve Zero Trust’s ability to identify and respond to security threats by analyzing user behavior and network activity for unusual patterns.
- Automated Policy Management: AI will help automate the creation and enforcement of security policies, reducing errors and ensuring consistent application.
- Adaptation to New Technologies:
- 5G and Edge Computing: Zero Trust will address security challenges posed by 5G and edge computing, ensuring secure access to data and devices at the network’s edge.
- Cloud Security: As cloud use grows, Zero Trust will be crucial for securing multi-cloud environments by enforcing consistent security measures across different cloud providers.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
- Behavioral Analytics: Constant monitoring of user and device behavior will allow real-time adjustments to security measures based on activity.
- Microsegmentation: Dividing networks into smaller segments will help prevent attackers from moving laterally and accessing sensitive data.
- Focus on Compliance and Risk Management:
- Regulatory Compliance: Zero Trust will help organizations meet stricter data protection laws by enforcing tight access controls and maintaining detailed logs of user activity.
- Risk-Based Access Control: Future Zero Trust models will use risk assessments to adjust access based on the current threat environment.
- Challenges:
- Implementation Complexity: Moving to Zero Trust can be difficult, especially for organizations with older systems. A step-by-step approach and collaborative teams will be fundamental.
- User Experience: Balancing strong security with a good user experience is essential. Organizations must secure data without creating too much hassle for legitimate users.
Final Words
Zero Trust Security is crucial in 2024 as cyber threats become more advanced. It protects sensitive data by always verifying users’ identities and limiting access based on strict rules. The future of Zero Trust includes using AI to detect threats better and adapting to new technologies like 5G and cloud computing. Implementing Zero Trust can be tough, especially for companies with older systems. However, its benefits in boosting security, meeting compliance needs, and supporting remote work make it an important part of modern cybersecurity.