Alaska is a land of untamed beauty, where towering mountains meet icy waters teeming with life. It’s a paradise for nature lovers and those who rely on its rich marine resources for their livelihoods. From the iconic salmon to the mighty halibut, Alaska’s fishing industry is the backbone of many local communities, driving cultural traditions and economic prosperity.
However, with such abundant resources comes the responsibility to protect them for future generations. Overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change pose significant challenges, making it crucial to have well-defined regulations. Fortunately, Alaska has some of the most forward-thinking fishing laws in the world—laws designed to strike a balance between ecological responsibility and economic opportunity.
These regulations enforce sustainable practices, ensuring that Alaska’s fishing industry thrives while safeguarding marine ecosystems and supporting local communities that depend on them.

Why Sustainable Fishing Matters
Sustainable fishing isn’t just a buzzword in Alaska; it’s a way of life. For centuries, indigenous communities have relied on fishing for food, cultural practices, and economic sustenance. Overfishing and habitat destruction pose significant threats to this traditional way of life, making it crucial for the state to implement laws that support long-term sustainability.
“Fishing isn’t just about catching fish; it’s about preserving a legacy for generations to come.”
Alaska’s fishing laws prevent overfishing, protect marine habitats, and ensure that fish populations remain healthy. This helps preserve the ecosystem’s delicate balance while supporting the livelihoods of thousands of Alaskans who depend on the fishing industry.

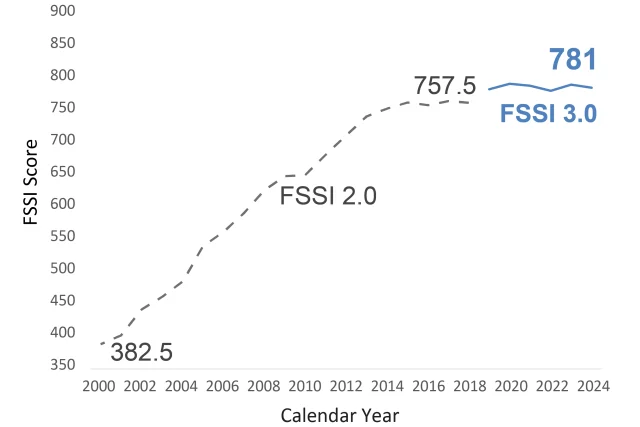
Fishing Stock Sustainability Index
Comparison of fish stock levels before and after regulations are as follows.
How Alaska’s Fishing Laws Work?
This is How the Fishing Laws Works
1. Catch Limits and Quotas: Keeping Fish Stocks Healthy
One of the most critical aspects of Alaska’s fishing laws is enforcing catch limits and quotas. These regulations ensure that fish stocks are harvested sustainably, preventing depletion. The Alaska Department of Fish and Game (ADF&G) works closely with scientists and fisheries managers to set quotas based on population assessments and reproductive rates.
In 2020, strict quotas helped increase sockeye salmon populations by 15% compared to previous years.

2. Seasonal Restrictions: Protecting Spawning Cycles
To protect fish during critical spawning periods, Alaska enforces strict seasonal restrictions. Fishing is prohibited or limited during these times to allow fish to reproduce and sustain their populations. For instance, salmon runs are carefully monitored, and fishing is only permitted when it does not interfere with natural spawning cycles.

Species | Spawning Season |
Steelhead | Late April – May |
Chinook Salmon | Late July – Early August |
Sockeye Salmon | Mid-July – Early August |
Pink Salmon | Late July – August |
Chum Salmon | Mid-June – September |
Coho Salmon | Late September – Early October |
Sheefish | Late September – Early October |
Burbot | Early Winter |
Pollock | Spring (varies with climate) |
3. Gear Restrictions: Fishing the Right Way
Alaska’s fishing laws regulate specific gear types to ensure sustainable fishing practices that protect marine ecosystems. Different fishing gear, such as trawl nets, longlines, and pots, have varying environmental impacts. Regulations aim to minimize bycatch—the unintentional capture of non-target species—by promoting the use of selective gear that reduces waste and supports species conservation.
“Using sustainable gear means protecting not just fish, but the entire ecosystem they support.”

Additionally, these laws help prevent habitat destruction by limiting gear that can damage sensitive marine environments like coral reefs and seafloors. By enforcing sustainable gear practices, Alaska not only safeguards fish populations but also maintains the delicate balance of the entire ecosystem, ensuring the long-term health of its fisheries.

4. Monitoring and Enforcement: Keeping Everyone Accountable
Alaska employs rigorous monitoring and enforcement measures to ensure compliance with fishing regulations. Observers are placed on commercial fishing vessels to collect data on catch composition, bycatch, and fishing practices. This data is then used to refine management strategies and ensure compliance with quotas and gear restrictions.

How Fishing Laws Benefit Local Communities?
Fishing isn’t just a business in Alaska—it’s a way of life. Many coastal communities depend on fishing for their economic well-being. Fishing impacts Alaska’s economy, and the state’s regulations are designed to protect these communities from the negative impacts of overfishing and market fluctuations.
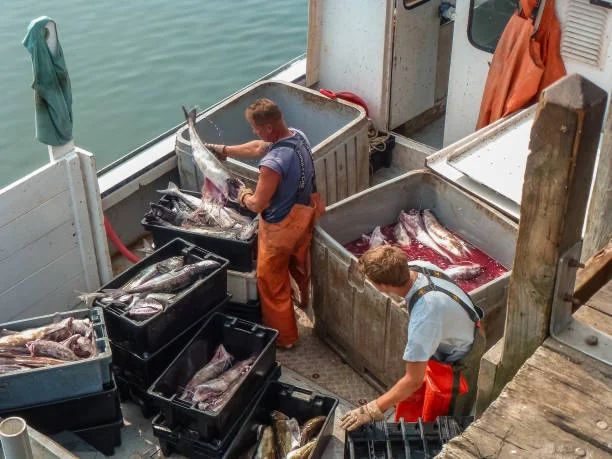
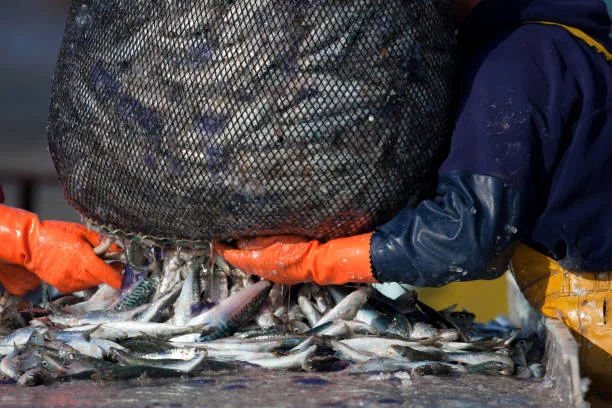


Safeguarding Wildlife and Ecosystems
Alaska’s fishing laws are about managing fish stocks and protecting the broader marine ecosystem. Overfishing can ripple effect on the entire food chain, impacting species such as seabirds, marine mammals, and even terrestrial wildlife that rely on healthy fish populations. The following information states how sustainable fisheries are ensured.

So we should take all necessary measures for sustainable fishing.

Challenges and Looking Ahead
While Alaska’s fishing laws are among the most effective in the world, challenges remain. Climate change is causing shifts in fish distribution and abundance, forcing managers to adapt regulations to changing environmental conditions. Additionally, illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing remains a persistent threat that requires ongoing vigilance.

Conclusion
Alaska’s fishing laws are crucial in preserving local communities and the environment. The state ensures its fisheries remain sustainable and productive by enforcing strict quotas, seasonal restrictions, gear regulations, and monitoring practices.
“By following these laws today, we secure a thriving future for Alaska’s fishing heritage.”











