Nowadays, we are constantly surrounded by information—whether it’s in books, online, or through conversations. But not all of it is true. This is why it’s important to know how to tell if a statement is true or false. Being able to identify the truth helps us make better decisions, avoid misunderstandings, and improve our learning.
For example, when you’re studying for an exam or taking a quiz, you often come across questions asking, “Which of the following statements is true?” Understanding what makes something true can help you answer these questions correctly. This concept of truth is used in many areas, such as science, law, history, and even everyday life.
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements is True? What Does It Mean?
The process of determining whether a statement is true involves evaluating it based on several key types of truth:
1. Factual Truth
Factual truth refers to statements that are based on real-world facts, which are verifiable through evidence. For example:
2. Logical Truth
Logical truth involves reasoning that holds up under scrutiny, meaning that it is consistent and doesn’t contain any contradictions. For instance:
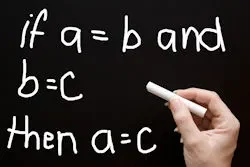
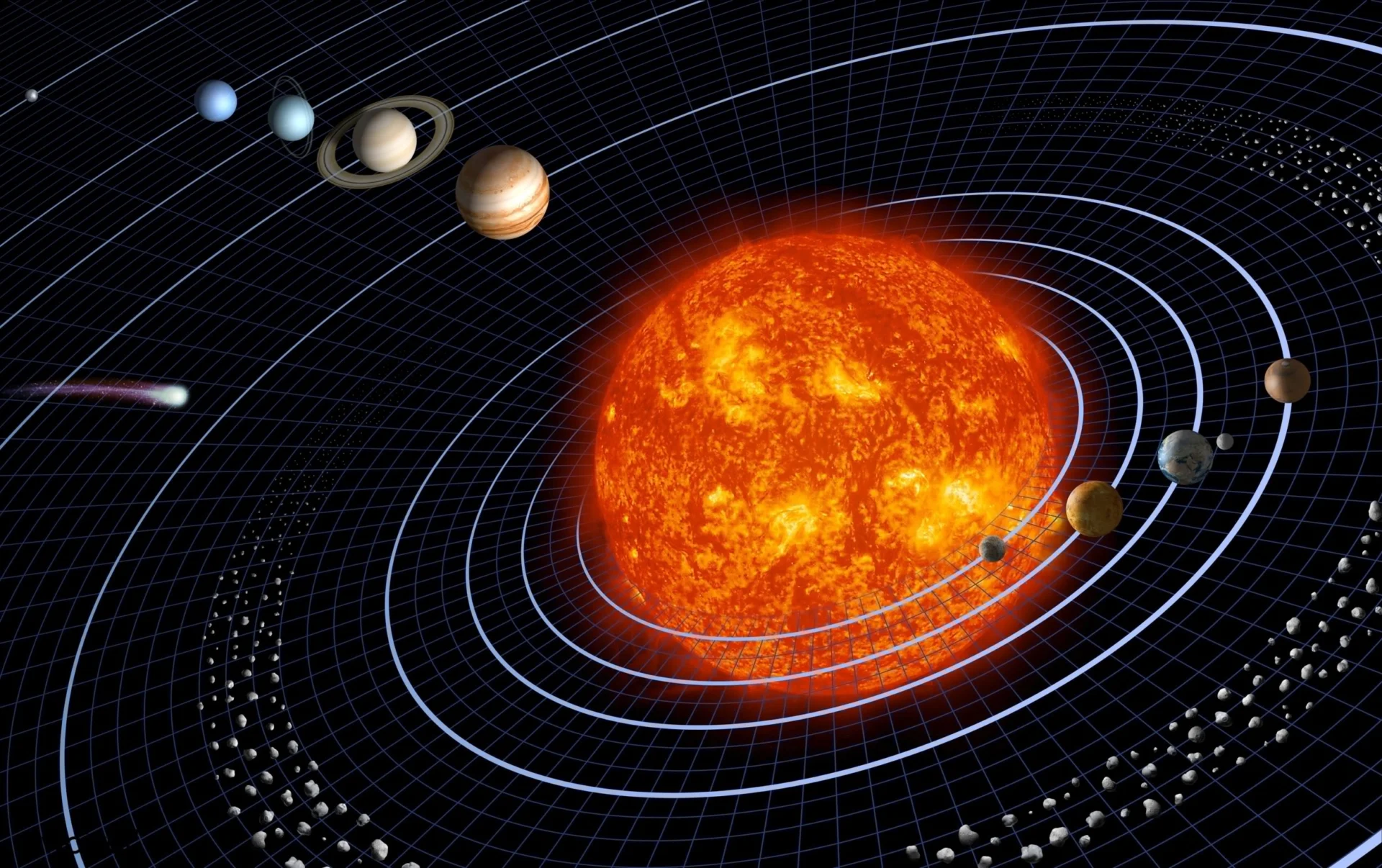
3. Scientific Truth
Scientific truth is derived from experimental evidence and peer-reviewed research. For example:

Common Methods to Verify Truth
To verify whether a statement is true, there are several methods we can use:
Checking Evidence
Logical Consistency
Expert Validation
Comparing to Established Knowledge
Prevalence of Misinformation
It’s important to note that misinformation is a widespread issue today. According to a 2024 Pew Research Center report, 73% of Americans encountered inaccurate news coverage about the 2024 presidential election at least somewhat often, highlighting how pervasive misinformation has become in the modern media landscape.
Examples of True vs. False Statements
One of the easiest ways to understand truth is by comparing true statements to false ones. Here’s a table that illustrates this:
True Statement | False Statement |
“Water freezes at 0°C.” | “Water freezes at 10°C.” |
“Paris is the capital of France.” | “Berlin is the capital of France.” |
“The Earth revolves around the Sun.” | “The Sun revolves around the Earth.” |
“Cats are mammals.” | “Cats are reptiles.” |
How to Identify the Truth in Different Contexts?
Truth can be identified differently depending on the context. Here are some examples:

In mathematics, truth is verified through proofs. Statements are true if they can be logically proven within a given mathematical system. For example, the Pythagorean Theorem is universally accepted because it can be rigorously proven.
In science, truth is determined through controlled experiments, peer-reviewed studies, and evidence. Scientific truths evolve as new evidence comes to light. For instance, the law of gravity was once only a theory, but after extensive testing and observation, it became an established scientific truth.

In law, truth is determined based on facts, evidence, and legal definitions. In ethics, truth may be subjective and based on moral perspectives. For example, a legal truth could be the verdict in a court case, while an ethical truth could involve the moral implications of that verdict.

Philosophical discussions about truth often delve into different interpretations of what constitutes "truth." Philosophers may debate whether truth is objective or subjective, depending on their worldview.
Answering Exam and Quiz Questions
For students, answering questions about which statement is true can be tricky, especially in multiple-choice exams. Here are some tips to help:
Pay attention to the wording of the question and eliminate statements that are obviously false. Context clues, such as the subject matter or key terms in the question, can guide you toward the correct answer.
Look for statements that align with what you know to be true based on your studies. For example, in a history exam, you’d know that “The Declaration of Independence was signed in 1776” is true, based on what you’ve learned in class.

The Importance of Critical Thinking in Choosing the True Statement
Critical thinking is essential for evaluating and selecting true statements. It helps us assess evidence, identify biases, spot logical fallacies, and compare sources. Without it, we risk accepting false or misleading information.
- Evaluates Evidence: Ensures statements are backed by facts and research.
- Identifies Biases: Helps recognize biased or skewed information.
- Spots Logical Fallacies: Detects errors in reasoning.
- Compares Sources: Verifies consistency with trusted, reputable sources.
Conclusion
Understanding what makes a statement true is vital in various areas of life, from academics to everyday decision-making. By applying logical reasoning, checking evidence, and consulting experts, we can better evaluate the truthfulness of statements. Developing the skill to think critically and verify information is key to navigating a world filled with varying opinions and conflicting facts.
Before accepting any statement as true, take a moment to evaluate it carefully. Fact-checking and critical thinking are essential practices in ensuring that the information we rely on is accurate and trustworthy.
FAQs
A statement is true if it accurately reflects reality and can be verified through evidence, logical consistency, or scientific proof.
Truth can be verified by checking evidence, ensuring logical consistency, consulting expert opinions, and comparing the statement to established knowledge.
Truth is objective and verifiable, while belief is subjective and can be influenced by personal opinions or experiences.