The global economy is set to grow significantly, with emerging markets leading the way. The latest forecast from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), published in April 2024, shows that many countries will see rapid economic growth in the next five years. The report points out that the top-performing economies are mainly in Africa and Asia, highlighting their strong potential for growth.
One important measure in the IMF’s forecast is the compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Simply put, CAGR shows a country’s average annual economic growth rate over a set period, considering the effect of compounding. This means the growth rate is applied to an increasing base yearly, offering a clearer view of steady growth over time.
This forecast underscores the importance of fastest growing markets in the global economy and highlights their growing influence. As these nations continue to advance, they present substantial opportunities for investors and promise significant enhancements in the quality of life for their citizens.
Role of Emerging Markets in the Global Economy
Emerging trends in market that are getting more important in the world economy. Think of places like Guyana, Ethiopia, India, and others. They’re called ’emerging’ because they’re still growing and getting stronger. Their role in the global economy means how much they affect trade, investments, and overall economic growth worldwide. So, understanding what they’re doing and how they’re growing is essential for everyone.
Top 10 Fastest Growing Emerging Markets
The top 10 fastest-growing markets are countries experiencing rapid economic expansion and development. These include nations like India, which has a booming technological industry and a growing middle class. Other notable rising markets include Bangladesh, where infrastructure investments are driving growth, and Vietnam, which is becoming a key player in global manufacturing.
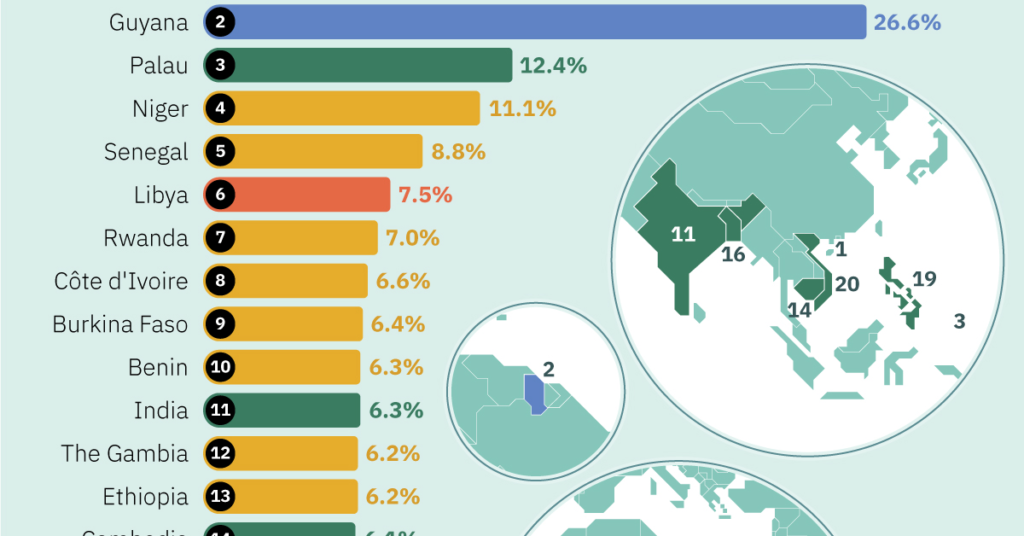
1- Guyana
Guyana, a small South American nation, is experiencing remarkable growth with a (CAGR) of 19.8%. This impressive growth is predominantly fueled by its burgeoning oil sector, which now produces 645,000 barrels daily (BPD). Despite its geographical location in South America, Guyana maintains strong ties with the Caribbean as a founding member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
Its economic vitality stems from abundant natural resources, including fertile agricultural lands, valuable minerals such as bauxite and gold, and vast tropical forests covering 80% of the country. Moreover, recent discoveries of offshore oil and gas reserves promise further economic expansion and diversification. Projections indicate that by 2028, Guyana is set to lead in crude oil production per capita, marking a significant milestone in its financial trajectory.
2- Mozambique
Mozambique, an African nation on the rise, is projected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9%. Renowned for its abundant resources, including fertile land, water, energy, and minerals, Mozambique recently gained attention for its significant offshore natural gas discoveries. The country boasts three deep seaports, pivotal for neighboring landlocked nations seeking access to global markets.
These ports serve as vital conduits for trade, enhancing regional economic integration and development. Furthermore, Mozambique maintains a robust economic partnership with South Africa, bolstering mutual growth and stability in the area. In 2023, Mozambique’s economy expanded by 5%, primarily attributed to the commencement of Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) production and notable growth in agriculture and services sectors, notably transport. This growth offset declines in manufacturing and construction activities, underscoring Mozambique’s resilience and potential for further economic advancement.
3- Rwanda
Despite facing obstacles such as declining external demand and efforts to manage inflation, Rwanda maintains a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. With ambitious goals of attaining Middle-Income status by 2035 and High-Income status by 2050, Rwanda has implemented a comprehensive seven-year National Strategies for Transformation (NST) framework aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Despite challenges, the economy experienced robust growth, expanding by 7.6% in the initial three quarters of 2023. This growth was fueled by resilient domestic demand and a resurgence in the industrial sector, underscoring Rwanda’s determination and potential for sustained economic advancement.
4- Bangladesh
Bangladesh has made impressive economic strides over the last twenty years, propelled by various factors, including a favorable demographic profile and thriving export industries such as ready-made garments (RMG), contributing a significant 85% to total exports.
Despite starting as one of the world’s poorest nations in 1971, Bangladesh achieved lower-middle-income status in 2015 and is now on course to graduate from the UN’s Least Developed Countries list by 2026.
Notable achievements in poverty alleviation and advancements in human development indicators, such as reductions in infant mortality and literacy rates, underscore Bangladesh’s remarkable journey towards prosperity and growth.
5- Ethiopia
With a (CAGR) of 6.7%, Ethiopia emerges as one of Africa’s rapidly expanding economies. It boasts a population of 126.5 million, the continent’s second-largest. Over the past fifteen years, Ethiopia has maintained an impressive growth trajectory, averaging nearly 10% annually, primarily fueled by substantial investments in public infrastructure.
Aligned with the 2019 Home-Grown Economic Reform Agenda, the government has devised a 10-year Development Plan to sustain robust growth, transition towards a private-sector-led economy, and enhance efficiency in critical sectors such as energy, logistics, and telecommunications. Additionally, the plan prioritizes initiatives to improve the business environment and tackle macroeconomic challenges, reflecting Ethiopia’s commitment to fostering sustainable development and prosperity.
6- Niger
As per the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Niger is anticipated to witness economic growth in the forthcoming years. Despite existing challenges, the country’s economy is poised to expand at a rate of 6.7% annually, propelled by advancements in agricultural output and strategic investments across critical sectors.
This growth trajectory is anticipated to persist, with forecasts indicating a growth rate of 6.9% in 2024 and sustained progression in the subsequent years. Despite persistent hurdles, such as elevated poverty levels, the IMF’s forecasts paint a hopeful picture for Niger’s economic outlook, presenting opportunities for enhanced economic diversification and improved standards of living for its populace.
7- Uganda
Despite facing external challenges, Uganda’s economy has exhibited resilience, showing a slight uptick in growth. In the initial quarter of 2024, the GDP saw a 5.3% expansion, propelled by a construction boom linked to oil activities and strong agricultural performance, notwithstanding erratic weather patterns.
Throughout the year, the country witnessed a surge in job creation and private investment, consistently bolstering domestic demand. The sustained increase in production, fresh orders, and employment during this prolonged period of prosperity underscores Uganda’s ability to propel its economy forward.
8- India
India, boasting a population exceeding 1.4 billion, stands as the world’s largest democracy and holds a pivotal role in the global economic landscape. Over the past decade, its integration into the global economy has fueled substantial economic expansion, positioning it among the fastest-growing economies globally.
India aims to achieve high middle-income status by 2047 and strive for net-zero emissions by 2070. Noteworthy strides have also been made in poverty alleviation, with the country successfully halving extreme poverty between 2011 and 2019.
9- Vietnam
Vietnam has transformed remarkably, transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a market-driven economy. This shift has propelled the nation out of extreme poverty and into lower middle-income status, establishing it as one of East Asia’s most vibrant emerging economies.
In recent decades, Vietnam has experienced a significant surge in GDP per capita, marking a six-fold increase and highlighting its substantial economic advancement. The agriculture sector has been instrumental in driving this growth, maintaining an annual growth rate of 2.5 to 3.5 percent. Contributing 13 percent to GDP and employing 29 percent of the population in 2021, the agriculture sector has facilitated economic expansion and ensured food security for the nation.
10- Senegal
Despite grappling with challenges such as political tensions and ongoing inflation issues, Senegal continues to stand out as one of the rapidly advancing emerging market economy. With a commendable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3%, Senegal underscores its economic potential on the global stage.
Despite persisting structural vulnerabilities, notably low productivity and limited human capital, Senegal remains dedicated to diversification and significant investment in crucial sectors like agriculture and energy, paving the way for future growth prospects.
While setbacks in hydrocarbon production may pose short-term obstacles, they also present promising opportunities for sustainable development and prolonged economic expansion. Overall, Senegal’s growth trajectory positions it as an attractive hub for investment ventures and developmental initiatives.
Future Of Emerging Markets
Understanding global economic trends and the role of emerging markets is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern economy. As emerging economy markets continue to grow in influence and significance, they present opportunities and challenges for businesses, investors, and policymakers.