Edge computing is increasingly recognized as a transformative technology for the Internet of Things (IoT) and the development of smart cities. Processing data closer to where it is generated enhances efficiency, reduces latency, and supports real-time decision-making. Let’s have a detailed look at its role and impact on IoT and smart cities.
The Role of Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing solves many challenges IoT (Internet of Things) systems face, especially regarding data processing and transmission. Here’s how this technology is transforming the IoT landscape:
Real-Time Processing and Low Latency:
One of the biggest advantages of edge computing is its ability to process data in real-time. This is extremely important for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart healthcare systems, where quick decisions can be crucial for safety.
- It processes data closer to its source.
- Reduces the distance data travels.
- This results in lower delays or “latency.”
- Faster than traditional cloud computing.
The edge computing market is growing rapidly, with predictions that it will expand at an annual growth rate of 26.5% from 2023 to 2028. This shows that more industries, especially those using IoT, are considering the value of its solutions.
Energy Efficiency:
IoT devices, like batteries, often run on limited power, so managing energy consumption is crucial. This technology helps by processing data locally, which means less energy is used to send data to distant cloud servers.
This local processing saves energy and extends the battery life of IoT devices. This is especially important as more IoT devices are deployed in various environments.
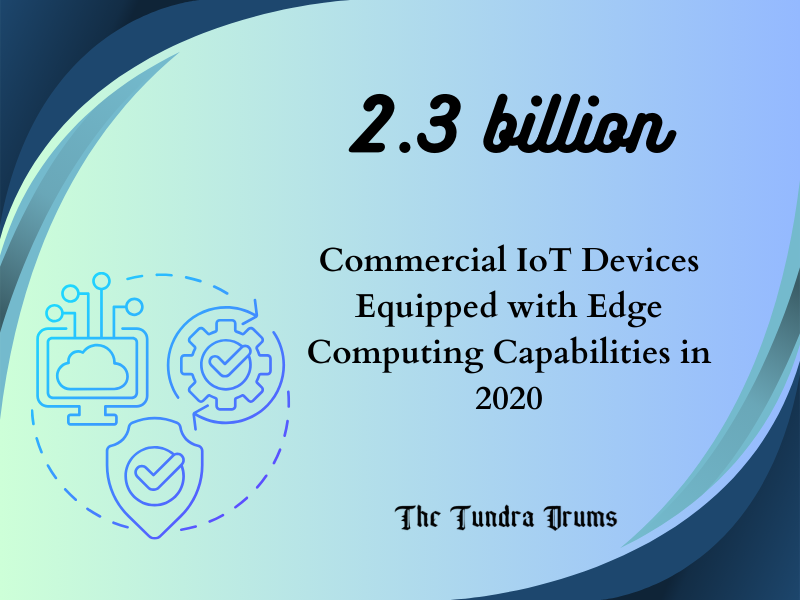
In 2020, about 2.3 billion commercial IoT devices equipped with its capabilities were in use, and this number will grow significantly in the coming years.
Scalability:
As cities and industries become more connected, the amount of data generated is skyrocketing. Edge computing makes it easier to manage this data by bringing computational power closer to where it is produced.
This is particularly important in crowded urban areas, where thousands of sensors and devices generate data simultaneously. This technology allows these systems to scale up efficiently without overwhelming central cloud systems.
The Role of Edge Computing in Smart Cities
This is also a key technology in smart cities’ development and smooth operation. It enhances many urban services and infrastructures, making cities more efficient and livable. Here’s how:
Enhanced Data Processing and Decision-Making:
Smart cities rely on sensors and IoT devices to monitor traffic flow and energy consumption. Edge computing allows these devices to process data right where it’s collected, which leads to faster and more accurate decision-making. For example, it can help optimize traffic signals based on real-time data, reducing traffic jams and improving vehicle flow.
Security and Privacy:
With so much data collection in smart cities, security and privacy are major concerns. It addresses these issues by reducing the amount of sensitive information that needs to be sent over the Internet. By processing data locally, cities can better protect citizens’ privacy and minimize the risk of data breaches.
Sustainability:
Edge computing also contributes to sustainability efforts in smart cities. It helps save energy by reducing the need to send large amounts of data to remote cloud servers. Additionally, it can work with local renewable energy sources, making city infrastructure more environmentally friendly.
Market Applications of Edge Computing in Smart Cities

The use of this technology in smart cities is growing fast. It currently makes up about 23% of the total edge computing market. This includes applications like urban management, traffic optimization, and public services. The largest share of edge computing use, about 30%, is in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), showing how versatile this technology is.
The Edge Computing in IoT will reach $23.4 billion by 2025, with significant growth outside major regions like North America and Asia-Pacific. This growth highlights the increasing importance of this technology worldwide.
Conclusion
Edge computing plays a crucial role in the future of IoT and smart cities. Its ability to process data in real time, enhance security, and promote sustainability makes it an essential component of modern urban infrastructure. As cities continue to evolve and adopt smart technologies, integration will be vital for optimizing urban services and improving residents’ quality of life.