Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting any supplement, including berberine, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
In recent years, the use of natural supplements has seen a significant rise in popularity across the UK, as more individuals seek alternatives to traditional medicine to enhance their well-being. Among various natural compounds gaining attention, berberine stands out due to its potential health benefits. In the same vein, dietary supplements like VitaBright Biotin tablets have also seen increased usage across the UK, particularly for promoting hair growth and overall health. However, this article will delve into the emerging health trend of berberine. So what is berberine, and why has it become a staple in the cabinets of the health-conscious population in the UK?
What is Berberine?
Berberine is a bioactive compound found in several plants, including European barberry, goldenseal, and tree turmeric. Both traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda have utilized it for centuries to treat a variety of conditions; however, it is only recently that modern science has begun to validate the health benefits of this ancient remedy. A study reveals that berberine operates at the cellular level by activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which triggers alterations in metabolic enzymes and glucose utilization. Its best researched benefit is in blood sugar control, which would be of special concern to those dealing with Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. “The potential magnitude of benefit is particularly striking in the UK, where a steady rise in the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes has been seen. This potential benefit is especially poignant in the UK, where approximately 4.6 million people are diagnosed with diabetes, and an estimated 1.3 million remain undiagnosed.
What Research Suggests About Berberine
Blood Sugar Management
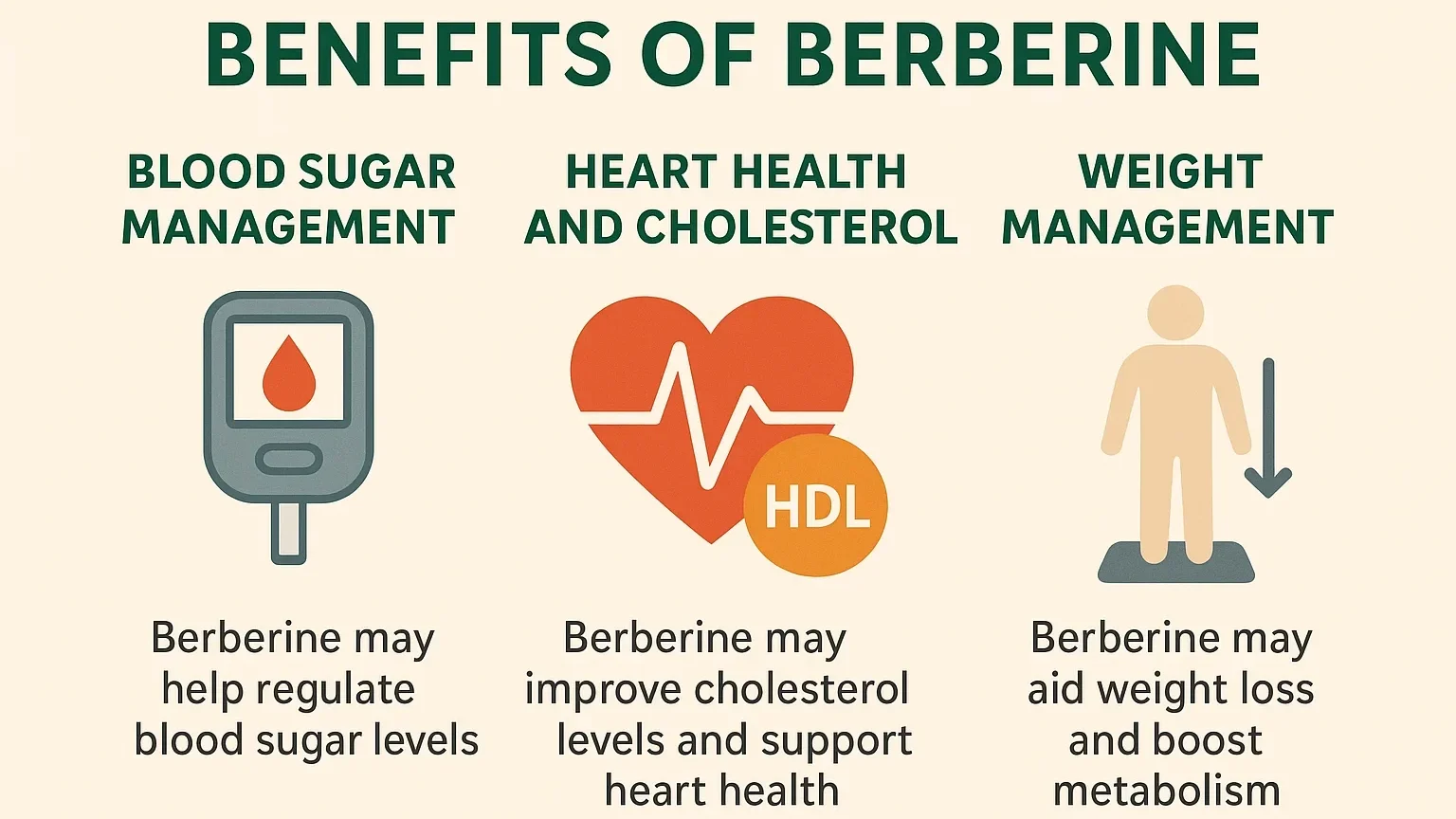
Another strong contributor to the spike in berberine popularity is its potential effects on cholesterol and cardiovascular health. Research has indicated that berberine may support healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which in turn may benefit the cardiovascular system. Research also suggests that it may elevate beneficial HDL (the “good” cholesterol) and improve artery function, both of which are crucial for maintaining long-term cardiovascular health. This aligns with the overall trend toward prevention in UK health strategies. And because heart disease is a leading cause of death, there are quite a few people out there eager to try natural solutions to keep the ol’ ticker ticking for longer.
Heart Health and Cholesterol
Research indicates that berberine may influence certain lipid markers, including total cholesterol and triglycerides. Some studies suggest potential improvements in HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels.
However, the evidence base includes a mixture of human trials and earlier-stage research. Differences in study design, dosage, and participant characteristics make it difficult to draw firm conclusions. While findings are promising, they are not definitive.
Weight Management

Although it seems that there is definitely something to be said about berberine, it is worth remembering that there are side effects and interactions to be aware of. Gastrointestinal problems (cramping, diarrhea, constipation) have been noted, especially at higher doses. For some users, nausea or stomach cramps may occur during the first couple of days of use. In addition, berberine may have interactions with prescriptions, mainly liver-metabolized prescriptions, and can affect blood pressure or blood sugar, along with prescription drugs. For this reason, those on medication or who are suffering from medical conditions should consult with a healthcare professional before adding berberine to their treatment regimens to ensure safe and effective inclusion in their overall health program. As a result, berberine may enhance metabolic rate and support fat loss, making it appealing to those seeking to achieve weight loss goals or manage obesity, a concern prevalent in the UK, where 64% of adults are classified as overweight or obese.
What the Evidence Quality Looks Like
One aspect often overlooked in discussions of supplements is the quality of the available evidence.
For berberine:
- Many studies involve relatively small participant groups
- Some research is conducted in animals or laboratory settings
- A number of trials are short-term
- Larger, multi-centre, long-term human trials are limited
This does not mean that berberine is ineffective; rather, conclusions should be tempered. Ongoing research will help clarify its long-term safety and effectiveness across different populations.
UK Regulatory Context: What Consumers Should Know
In the UK, dietary supplements are regulated as foods rather than medicines. This means:
- Products are not licensed in the same way as pharmaceutical drugs
- Formulations may vary between brands
- Quality control and ingredient concentration can differ
Consumers are encouraged to choose products from reputable manufacturers that provide transparent labelling and, where possible, third-party testing information. Awareness of regulatory distinctions helps set realistic expectations.
Safety and Precautions
The shift away from drugs toward natural plant-based remedies such as berberine follows a broader change to holistic health in the UK, with growing demand for natural alternatives to accompany traditional treatments. Consumers want to know they can trust that what they buy is sourced responsibly, made safely, and there’s third-party testing to ensure product quality. However, as with any supplement, it is crucial to find high-quality berberine. Selecting reputable brands that label honestly and are safety-certified supports efficacy and safety. By sourcing from a reputable supplier, you can help reduce risks from impurities or poor-quality products that could otherwise undermine health benefits and limit the potential benefits of supplementation.
Who Should Be Cautious?
Certain groups should exercise additional caution and seek medical advice before considering berberine:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals
- People taking prescription medication
- Individuals with chronic health conditions
- Those managing blood sugar or cardiovascular disorders
Supplement decisions are highly individual and should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider.
Supplements Are Not Replacements for Treatment
It is important to emphasise that dietary supplements are not substitutes for prescribed medical treatment, structured nutrition plans, or lifestyle interventions.
Factors such as balanced diet, physical activity, sleep quality, and stress management remain foundational to long-term health. Supplements, where appropriate, may complement these efforts, but they should not replace professional care.
Also Read: Nutrition, Activity & Culture: Modern Wellness in Traditional Places
Conclusion: An Emerging Area of Interest, Not a Definitive Solution
Berberine is increasingly discussed in UK health research due to emerging evidence of its potential metabolic effects. Some studies suggest potential benefits in blood glucose regulation, lipid markers, and metabolic pathways. However, the overall body of evidence remains mixed, with limitations in study size and duration.
As interest grows, informed decision-making becomes essential. Understanding the quality of research, the regulatory landscape, and potential risks allows individuals to approach supplementation thoughtfully.
Ultimately, berberine represents an evolving area of scientific study, not a guaranteed solution. Professional guidance and a balanced health strategy remain central to any long-term wellness approach.










